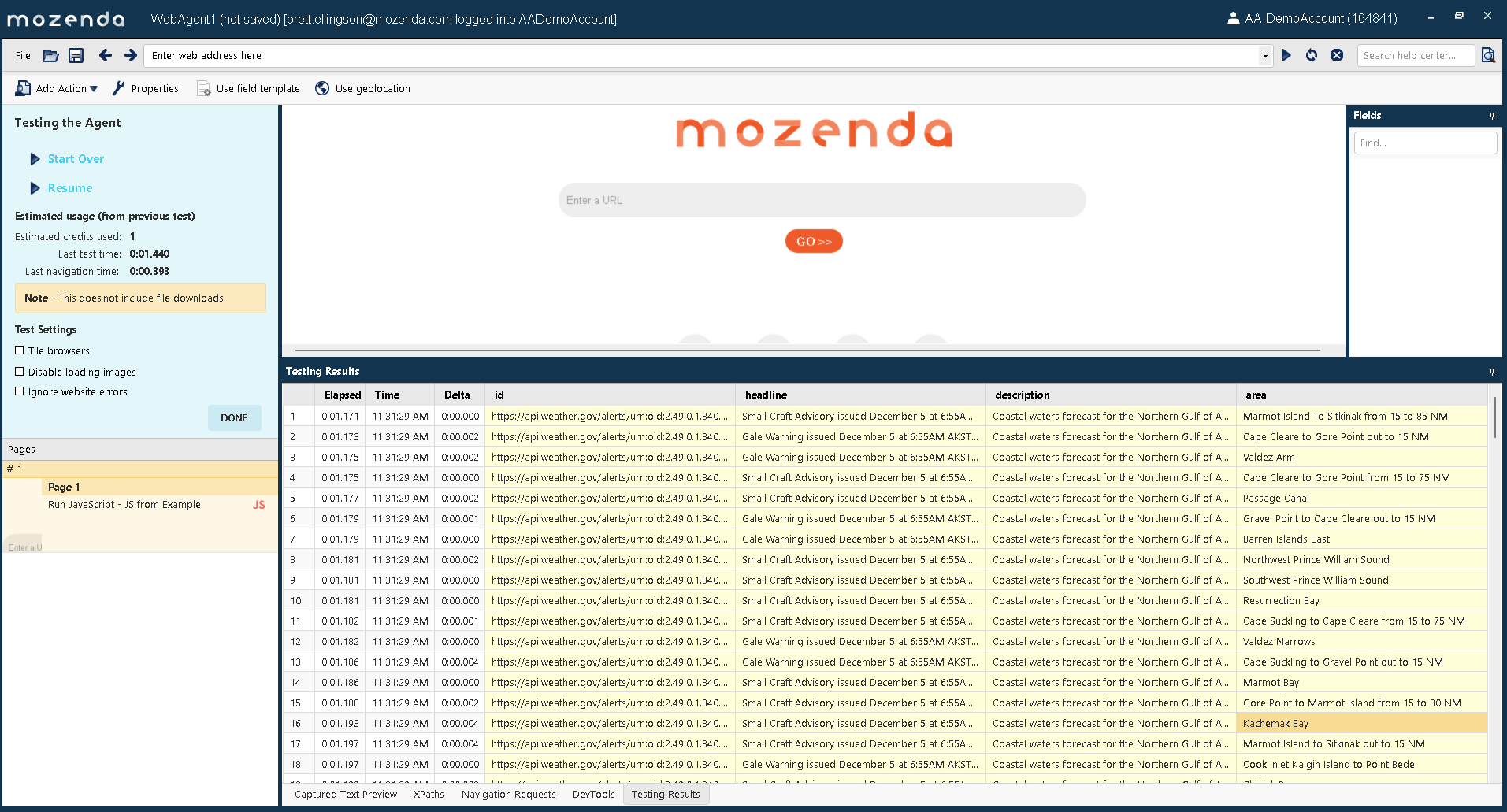
For this example, we will be scraping active weather alerts from the United States Weather Service. The purpose it to illustrate:
- Making a request to a web service that returns a JSON response
- Parsing that response
- Writing the parsed response to the Mozenda Agent Collection
Concepts that you should familiarize yourself with with to accomplish this are:
- Mozenda Run JavaScript action
- The JavaScript
fetchfunction
(async function () {
try {
// Request active weather alerts from the AL region
// This request returns a JSON-formatted response
// You can see the format by loading the URL in a browser
const url = 'https://api.weather.gov/alerts/active/region/AL';
const response = await fetch(url);
// Attempts to convert the JSON text response to a JavaScript
// object
const data = await response.json();
// Format the response to rows of objects as required by
// Mozenda's M_SetFieldValues() function
// Create an array to pass into M_SetFieldValues()
const rows = [];
// Iterate through the "features" array
for (const feature of data.features) {
const row = {};
row['id'] = feature.id;
const properties = feature.properties;
row['headline'] = properties.headline;
row['description'] = properties.description;
row['area'] = properties.areaDesc;
rows.push(row);
}
// console.log(rows);
// Write all rows from the response to the Mozenda
// Agent's output collection
M_SetFieldValues(rows);
M_StopWaiting();
} catch (err) {
M_StopWithError(err.name, err.message);
}
}
)();
To see the example in action, copy the above code to a RunJavaScript action, and test the Agent.