Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) is the standard language used to create documents made to display in a web browser. HTML uses nested sections to define and organize the content of the site, including images, links, and text. A web browser, like Chrome or Firefox, references an HTML document to render the webpage you see when you visit a URL.
HTML Element
An HTML element consists of an opening tag, the content, and a closing tag. These tags can be used to create a bulleted list, add a table, embed pictures and videos into the website, and much more. Below is a list of common tags you might see while web scraping. This is not an all-encompassing list and there are many more tags, so do not be alarmed if in your HTML journey you discover something new.
| Tag | Tag name | Description |
|---|---|---|
<p></p> |
Paragraph tag | Used to define paragraph content. |
<a></a> |
Anchor tag | Used to link one page to another page. |
<li></li> |
List tag | Used to list the content. |
<ul></ul> |
Unordered List tag | Used to list the content without order. |
<ol></ol> |
Ordered List tag | Used to list the content in numeric order. |
<img></img> |
Image tag | Used to add image elements - note that this is a single tag. This is because the image itself is embedded in the image tag. There is nothing to close off. |
<table></table> |
Table tag | Used to create a table. |
<th/th> |
Table header tag | Used to define the column header in a table. |
<tr/tr> |
Table row tag | Used to define a row in a table. |
<td/td> |
Table cell tag | Used to define the content cells in a table. |
<form> </form> |
Form tag | Used to create an html form. |
<h1> </h1> |
Header 1 tag | Used to define headings, this should only be used once per page. |
<h2> </h2> |
Header 2 tag | Used to define headings, usually a sub-header. |
<h3> </h3> |
Header 3 tag | Used to define headings. usually used for smaller sub-header. |
<em></em> |
Emphasis tag | Used to define emphasis (italicized) on a word(s). |
<b></b> |
Bold tag | Used to define bold text. |
<div></div> |
Divider tag | Typically used to divide the website into different sections. |
Attribute / Value
An HTML element can include an attribute that controls or modifies its behavior. Attributes generally display as name-value pairs, where the attribute name and value are separated using =.
In the example HTML below, the <span> element includes the <class> attribute and the “price”value:
<span class="price">29.99</span>
HTML Structure:
HTML documents use a hierarchy similar to a family tree to organize content, so it's common to use family terms to describe the relationship between elements. A parent is any element that contains one or more child element, and child elements are typically indented under their parent element.
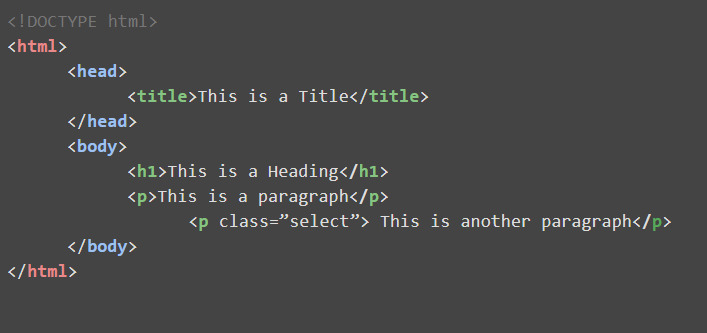
Let's start at the top:
- Parent element:
- HTML is parent to head and body.
- head is parent to title, while body is parent to h1* and p.
- Sibling element
- head and body are siblings.
- h1 and p are siblings.
- Child element
- title is a child to head.
- h1 and p are children to body.
- Grandparent/ancestor:
- HTML is a grandparent or ancestor to title, h1 and p.
Why it matters
The better you understand HTML, the easier it is to create effective web harvesting agents. A grasp of HTML elements and their place within a hierarchy allows you to create and customize XPath expressions that facilitate consistent and clean data capture.