There are several ways to write an XPath expression to capture the information from an HTML element. Adopting different strategies, depending on the structure of web page, can help you capture the data you want more reliably.
XPath is a query language made up of location steps that help you and your agent find the data you need. There are three components to an XPath:
- Axis
- Node
- Predicates or filters
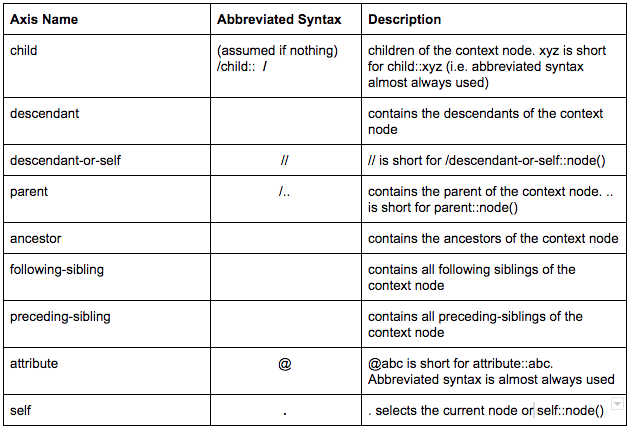
Common axis names
The axis represents a relationship to the current node and is used to locate nodes relative that node on the tree.
| Axis name | Abbreviated syntax | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ancestor:: | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node. | |
| ancestor-or-self:: | Selects all ancestors (parent, grandparent, etc.) of the current node. | |
| attribute | @ | Selects all attributes of the current node. |
| child | /child:: or / | Selects all children of the current node. |
| descendant:: | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node. | |
| descendant-or-self:: | // | Selects all descendants (children, grandchildren, etc.) of the current node and the current node itself. |
| following-sibling:: | contains all following siblings of the context node. | |
| parent:: | /.. | contains the parent of the context node. Use .. for the short hand of parent::node(). |
| preceding-sibling:: | Selects all nodes that appear before the current node in the document, except ancestors, attribute nodes and namespace nodes. | |
| self:: | . | . selects the current node or self::node(). |
| normalize-space | normalize-space( [string] ) | Removes any leading or trailing white-space from a string replaces it with a single space. |
Common filters/predicates:
To apply any function to your XPath expression you must add brackets next to the name of the HTML element. Multiple functions can be applied to one element.
Attribute selector: Use the attributes to identify an element.

Attribute contains function: Select some of the attributes value to find a match. This is helpful when the value is long or if there is a specific value string you want.

Text contains function: Instead of using an attribute use the text on the website to identify the element you want. For example, if you would like to select sponsored items, search for the word sponsored in the HTML and return the result.

Not contains: To exclude a specific element from your capture add a "not" before your "contains" function.

And - or: Add multiple functions to identify your HTML element. For example, if you want to select both the price and price shared the attribute of id="tv" and class="price", using both of these would narrow in the results to show the only those that matched both tv and price.

Number operator: Adding a number inside of brackets selects that HTML element based on numerical order. Selecting by numerical order is less reliable than specifying an element by an attribute such as class because the order of HTML elements can change.